The Importance of Wolf Skull
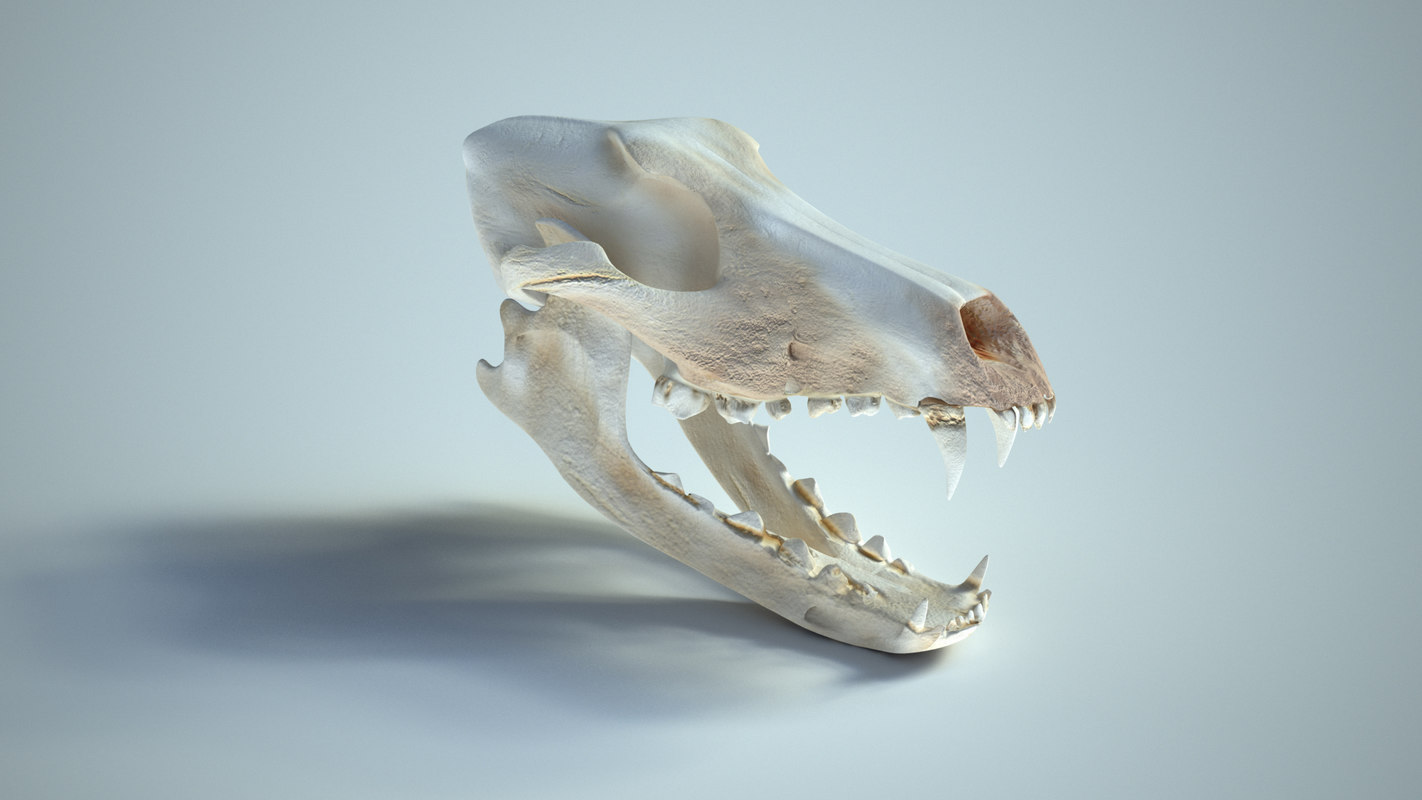
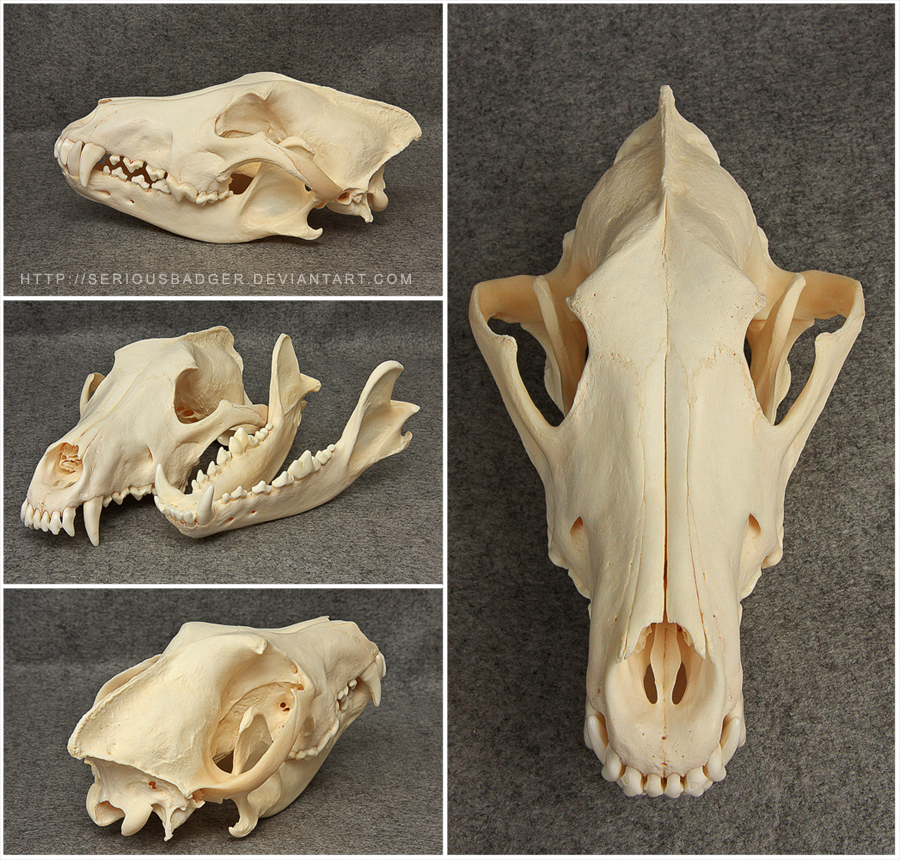
When it comes to understanding the anatomy and behavior of wolves, the wolf skull plays a crucial role. The skull of a wolf not only provides protection to its brain and sensory organs but also offers valuable insights into its diet, hunting techniques, and overall evolutionary adaptations.
Structure and Features
The wolf skull is an intricate structure that showcases numerous adaptations for its predatory lifestyle. Its most prominent feature is the elongated snout, which allows wolves to grasp and hold onto their prey with precision. Additionally, their powerful jaw muscles and sharp teeth enable them to tear through flesh and bone effortlessly.
Dental Adaptations
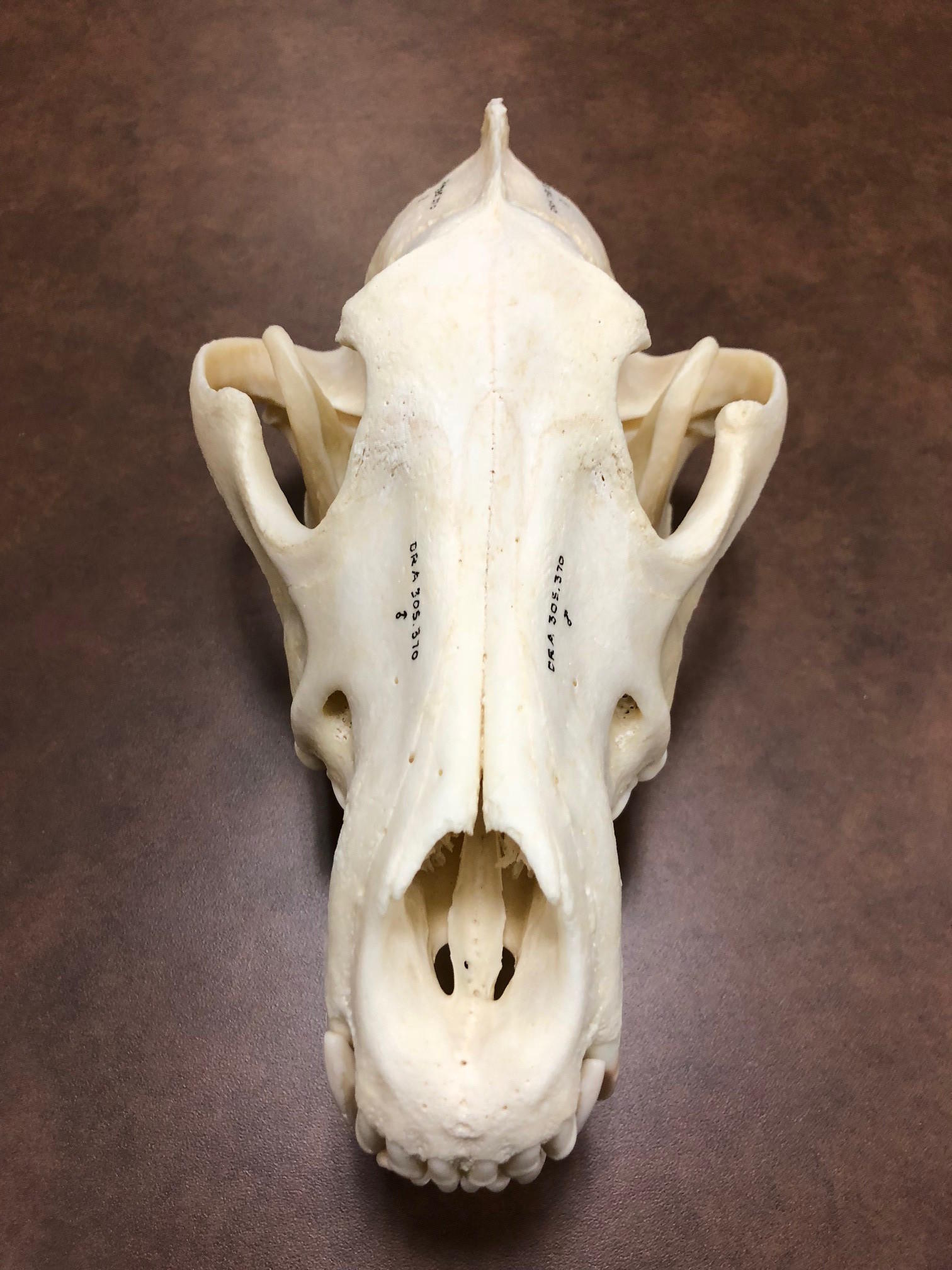
Examining the wolf skull's dental adaptations provides valuable insights into its diet. Wolves are carnivores with a preference for large ungulates like deer and elk. Their teeth are specialized for cutting, shearing, and crushing the bones of their prey. The presence of sharp incisors, long canines, and molars with sharp cusps reflects their role as efficient predators.

Sensory Organs and Vision
The wolf skull also houses essential sensory organs that contribute to their exceptional hunting abilities. Their eyes, positioned on the front of the skull, provide binocular vision, enabling accurate depth perception while stalking prey. The presence of a well-developed olfactory system, indicated by a large nasal cavity, allows wolves to detect scents from considerable distances.

Evolutionary Significance
The wolf skull's structure has evolved over time, adapting to various environmental factors and hunting strategies. Fossil records reveal a gradual transition from smaller, more generalized skulls to larger, more specialized ones. These adaptations have allowed wolves to survive and thrive in diverse habitats, from the Arctic tundra to the dense forests.

Conservation and Research
Studying wolf skulls not only contributes to our understanding of their biology but also aids in conservation efforts. By analyzing the size and shape variations in skulls, scientists can gather valuable data about different wolf subspecies and their distribution. This information assists in formulating effective conservation strategies for maintaining healthy wolf populations.