
Introduction
Wolves have long been an intriguing and captivating presence in our world. They are majestic creatures that have inspired myths, legends, and even fear throughout history. This article aims to provide a comprehensive reference to everything you need to know about wolves, from their behavior and habitats to their ecological importance and conservation efforts.

Behavior
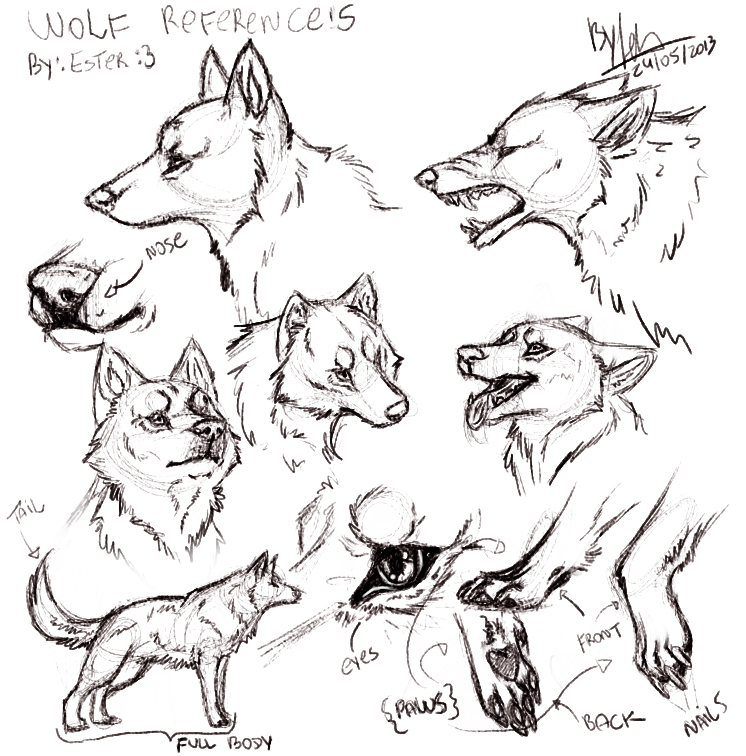
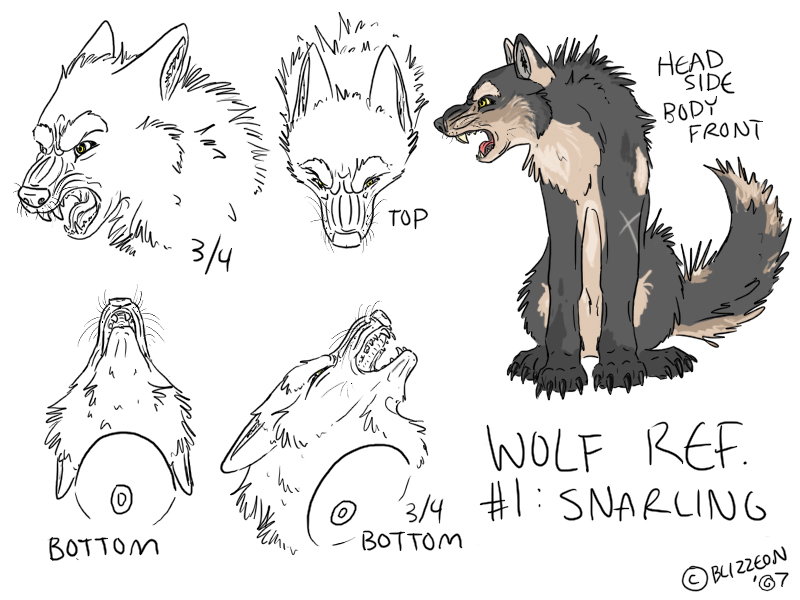
Wolves are highly social animals that live in packs. These packs consist of family members led by an alpha pair. They communicate through howling, body language, and scent marking. Wolves are known for their intelligence, hunting skills, and strong sense of loyalty.

Habitat
Wolves can be found in various habitats across the world, including forests, tundra, and grasslands. They have adapted to survive in diverse climates, from the Arctic to the deserts. Wolves are highly adaptable and can thrive in both wilderness areas and human-dominated landscapes.

Diet
Wolves are carnivores and primarily feed on large ungulates such as deer, elk, and moose. They are apex predators and play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance. Wolves also scavenge on carrion and occasionally prey on smaller mammals, birds, or fish.

Reproduction
Wolves typically mate for life and have a unique breeding season. The alpha pair leads the reproduction process within the pack. After a gestation period of around two months, the female gives birth to a litter of pups. The entire pack participates in raising and protecting the young.

Ecological Importance
Wolves play a vital role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. As apex predators, their presence helps control the population of herbivores, preventing overgrazing and promoting biodiversity. They also influence the behavior and distribution of their prey, leading to a cascading effect on the entire ecosystem.

Conservation Efforts
Due to habitat loss, hunting, and human-wildlife conflicts, wolves face numerous conservation challenges. Efforts are being made worldwide to protect and restore wolf populations. These include habitat conservation, reintroduction programs, and implementing measures to reduce conflicts between wolves and human activities.
Myths and Legends
Wolves have been deeply ingrained in human culture and folklore for centuries. They are often depicted as symbols of loyalty, cunningness, and spirituality. However, they have also been unfairly portrayed as villains in various myths and fairy tales. Separating fact from fiction is important when understanding the true nature of wolves.

Wolf-Dog Hybrids
Wolf-dog hybrids, also known as wolfdogs, are the result of breeding between wolves and domestic dogs. These hybrids possess a mix of wolf and dog characteristics, and their behavior can be unpredictable. It is important to understand the responsibilities and challenges associated with owning a wolfdog as a pet.

Human-Wolf Interactions
Human-wolf interactions have a complex history. While wolves evoke fear in some people, it is essential to recognize the importance of coexistence and understanding their ecological role. Educating communities about wolves and promoting responsible practices can help reduce conflicts and foster peaceful relationships.
Conclusion
Wolves are fascinating creatures that deserve our respect and protection. Understanding their behavior, habitat, and ecological importance is crucial for their conservation. By dispelling myths and promoting coexistence, we can ensure a future where wolves thrive in harmony with humans and the natural world.